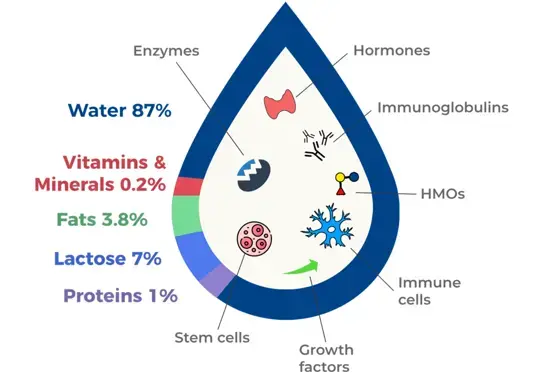
Articles and Books

The gut microbiota is an emerging target for improving brain health during ageing

Nutrition in school-age children: a rationale for revisiting priorities

Infant and Toddler Formulas Supplemented with 5 HMOs and Fed from Birth to 15 Months are Safe and Support Age-Appropriate Growth: A Randomized, Controlled Trial

Infant and Toddler Formulas Supplemented with 5 HMOs and Fed From Birth to 15 Months Modulate the Gut Microbiome Trajectory Towards That of Breastfed Infants

Early Life Gut Microbiome Development in Bangladeshi Infants, Its Association with Food Intake and Health Outcomes

Human Milk Macronutrient Composition During First Six Months of Lactation in Exclusively Breastfeeding Filipino Women

Annales Nestlé Article: Breastfeeding during a Pandemic

Breastfeeding Potentially Lowers Maternal Risk of Cardiovascular Events