Articles and Books

Understanding sustainable diets: a descriptive analysis of the determinants and processes that influence diets and their impact on health, food security, and environmental sustainability.

Lactation for Infant Feeding Expertise (LIFE) Abstract book

NNI News - Update: Allergies, Proteins, Malnutrition

Nestlé Research on Human Milk Oligosaccharides: Latest Update

2’fucosyllactose is well tolerated in a partially hydrolysed Whey Protein Infant Formula with a probiotic

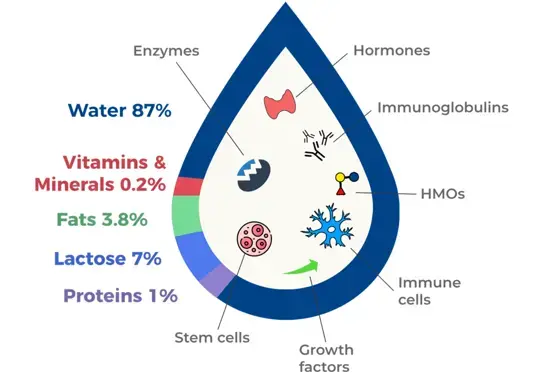
Human Milk Oligosaccharides: the Link between Mother’s and Baby’s Health

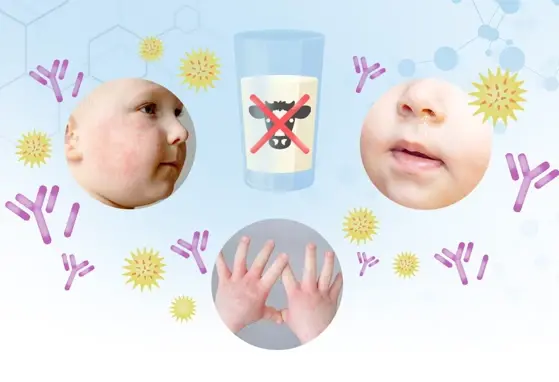
Babies fed Infant Formula with 2’FL had immune Biomarkers more like breastfed Babies

Benefits of two Human Milk Oligosaccharides, 2’Fucosyllactose and Lacto-N-Neotetraose in Infant Nutrition